A Beginner’s Guide to Smart Contracts
One of the best things about the blockchain is that, because it is a decentralized system that exists between all permitted parties, there’s no need to pay intermediaries (Middlemen) and it saves you time and conflict. Blockchains have their problems, but they are rated, undeniably, faster, cheaper, and more secure than traditional systems, which is why banks and governments are turning to them.
In 1994, Nick Szabo, a legal scholar, and cryptographer, realized that the decentralized ledger could be used for smart contracts, otherwise called self-executing contracts, blockchain contracts, or digital contracts. In this format, contracts could be converted to computer code, stored and replicated on the system and supervised by the network of computers that run the blockchain. This would also result in ledger feedback such as transferring money and receiving the product or service.
Start Your Free Trial Today
Free Trial
What are Smart Contracts?
Smart contracts help you exchange money, property, shares, or anything of value in a transparent, conflict-free way while avoiding the services of a middleman.
The best way to describe smart contracts is to compare the technology to a vending machine. Ordinarily, you would go to a lawyer or a notary, pay them, and wait while you get the document. With smart contracts, you simply drop a bitcoin into the vending machine (i.e. ledger), and your escrow, driver’s license, or whatever drops into your account. More so, smart contracts not only define the rules and penalties around an agreement in the same way that a traditional contract does, but also automatically enforce those obligations.
What is a smart contract
What is Blockchain Technology? A step-by-step guide than anyone can understand
As Vitalik Buterin, the 22-year-old programmer of Ethereum, explained it at a recent DC Blockchain Summit, in a smart contract approach, an asset or currency is transferred into a program “and the program runs this code and at some point it automatically validates a condition and it automatically determines whether the asset should go to one person or back to the other person, or whether it should be immediately refunded to the person who sent it or some combination thereof.”In the meantime, the decentralized ledger also stores and replicates the document which gives it a certain security and immutability.
Example
Suppose you rent an apartment from me. You can do this through the blockchain by paying in cryptocurrency. You get a receipt which is held in our virtual contract; I give you the digital entry key which comes to you by a specified date. If the key doesn’t come on time, the blockchain releases a refund. If I send the key before the rental date, the function holds it releasing both the fee and key to you and me respectively when the date arrives. The system works on the If-Then premise and is witnessed by hundreds of people, so you can expect a faultless delivery. If I give you the key, I’m sure to be paid. If you send a certain amount in bitcoins, you receive the key. The document is automatically canceled after the time, and the code cannot be interfered by either of us without the other knowing since all participants are simultaneously alerted.
You can use smart contracts for all sort of situations that range from financial derivatives to insurance premiums, breach contracts, property law, credit enforcement, financial services, legal processes and crowdfunding agreements.
Fonte e matéria completa:
https://blockgeeks.com/guides/smart-contracts/
Smart Contract – Uma analise jurídica
O Smart Contract a cada dia que passa ganha mais notoriedade, principalmente nas áreas envolvendo transações de compra e venda, e tem atraído olhares de muitos investidores e instituições financeiras ao redor do mundo.
O que é Smart Contract ou Contrato Inteligente?
Os contratos inteligentes permitem a você trocar dinheiro, propriedades, ações ou qualquer coisa de valor de uma maneira transparente e livre de conflitos, evitando os serviços de um intermediário.
A melhor maneira de descrever contratos inteligentes é comparar a tecnologia a uma máquina de venda automática. Normalmente, você procuraria um advogado ou um tabelião, pagaria e aguardaria enquanto recebia o documento. Os contratos inteligentes não apenas definem as regras e penalidades em torno de um contrato da mesma maneira que um contrato tradicional, mas também automaticamente impõem essas obrigações.
(Imagem: https://blockgeeks.com/)
O Smart Contract é ilegal?
Ainda que com suas peculiaridades formais, o contrato inteligente pode sim ser considerado pelo ordenamento jurídico como válido. Ao nos atentarmos ao Código Civil, art. 107º, observamos que não há necessidade de uma forma especial para se fazer um contrato (Princípio da Liberdade das Formas), sendo necessária a validade do negocio jurídico, podendo deixar de produzir efeitos jurídicos, e ser considerado nulo ou anulável caso não cumpra determinadas condições, tais condições estão expressas no art. 104° do Código Civil, e são:
I – agente capaz;
II – objeto lícito, possível, determinado ou determinável;
III – forma prescrita ou não defesa em lei.
Então mesmo que seja escrito por uma linguagem de programação, o contrato poderá ser válido.
Contudo mesmo que havendo essa liberdade formal concedida pelo código civil, não resta dúvidas de que a linguagem da programação em relação aos smart contract representa uma barreira para os operadores do direito e por grande parte da sociedade, pois para interpretar e montar um código exige uma perícia técnica que ainda não é acessível ao homem médio.
Problemas no Smart Contract
Como o contrato inteligente é executável de forma automática e imutável fica a dúvida a cerca de algumas situações, como a possibilidade de erro no código do contrato inteligente em relação à carteira (wallet)de uma das partes, ocasionando a suspensão da eventual obrigação contratada.
É necessário nos atentarmos a uma nova situação que surge em relação a rescisão judicial do contrato. O contrato inteligente por ser auto-executavel e imutável, não possui um intermediário e não pode ser alterado por nenhuma das partes. Caso ocorra um problema e uma das partes contratantes queira recorrer a justiça para rescindir o contrato, como ficaria? A decisão judicial seria ineficaz, pois o contrato iria prosseguir com o que foi planejado independentemente de fatores externos.
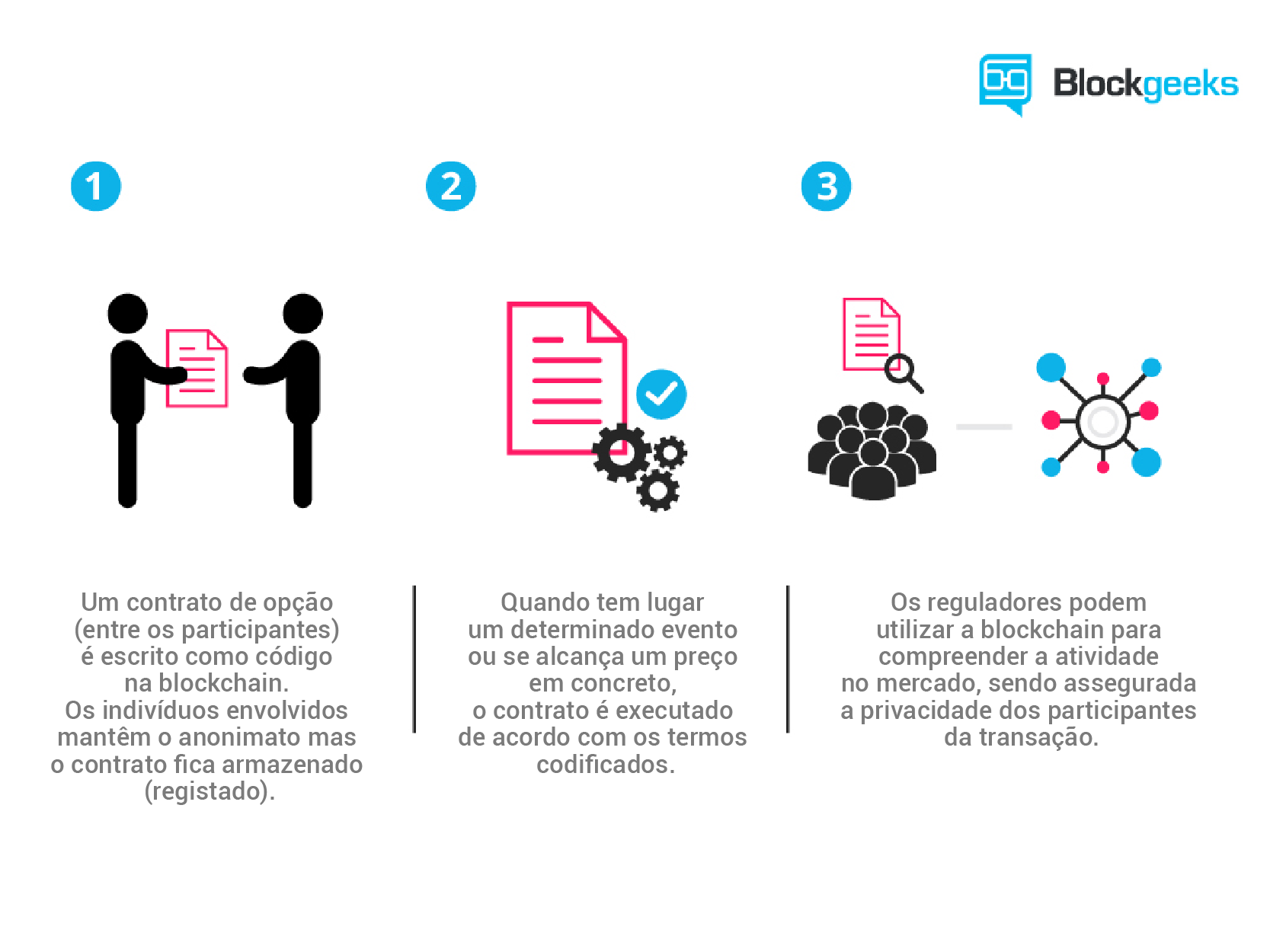
Uma questão a ser analisada também é a respeito ao anonimato dos indivíduos dentro do blockchain. Pois mesmo havendo o registro público de todas as suas movimentações financeiras, a identidade real de cada uma das partes está protegida por códigos criptografados dentro do blockchain. Desse modo, pessoas mal-intencionadas poderiam utilizar-se de tal recurso para esconder-se.
Regulamentação do Smart Contract
Até o momento não existem proposta legislativas que busquem controlar ou proibir smart contracts e uso do blockchain no Brasil, temos apenas projetos de lei como a PL 2305/2015 em relação às moedas virtuais.
Mesmo tendo um grande potencial, os contratos inteligentes ainda estão em estágio inicial de desenvolvimento. Mas acredita-se que futuramente esses contratos serão um importante instrumento para acelerar os negócios jurídicos.
Referencia
Fonte:
https://www.ab2l.org.br/smart-contract-uma-analise-juridica/

Nenhum comentário:
Postar um comentário